Beat Garden Blues and Bee Happy
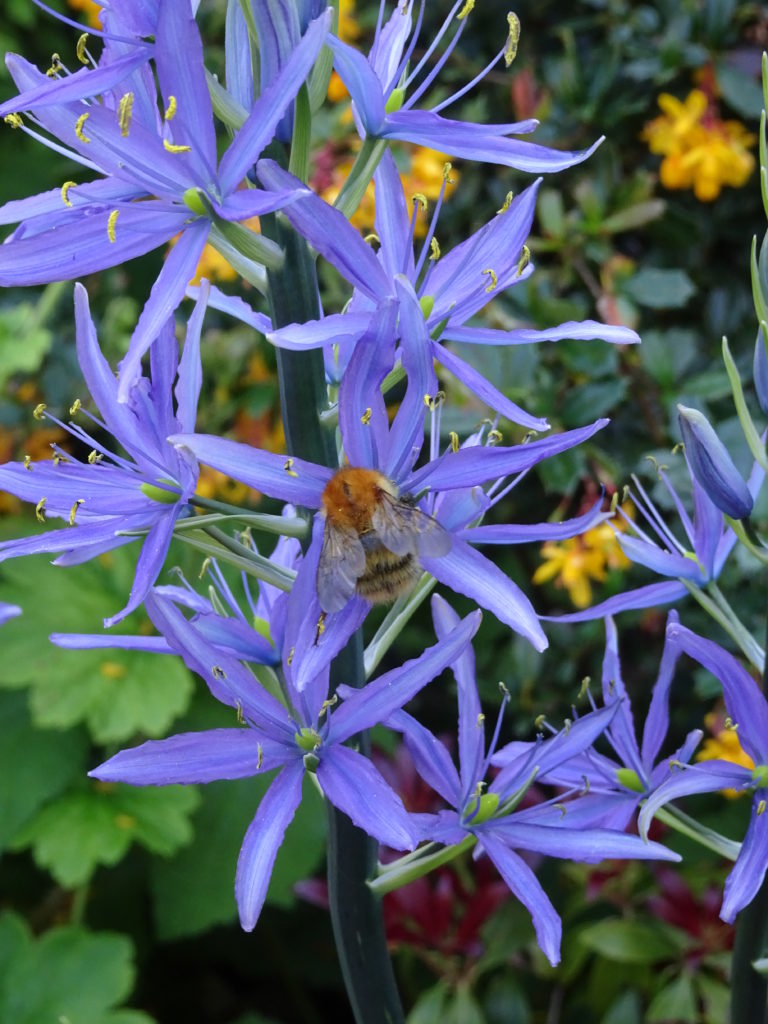
Rumour that Bees are in terminal decline is not borne out in my garden this year. The Bees seem very happy on the blue flowers and I am happy as it gives me an excuse to show some more blue photographs (of flowers!).
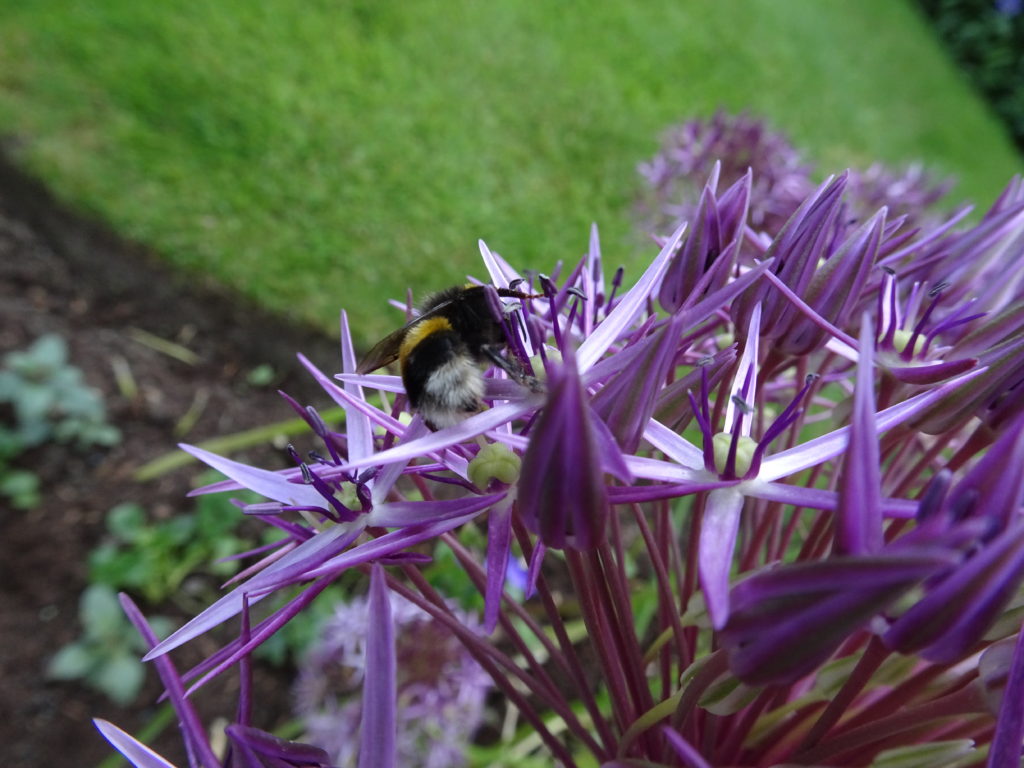

It is hard to be ‘blue’ when your senses are fully engaged.
- Creating a buzz provides a new sensory experience in the garden and it make a change from the sound of wind and the patter of rain.
- On the other hand I have just felt the pain from pruning a very prickly leaved Berberis that will now have fewer blue berries for the blackbirds later this year.
- The Californian Lilac below is exuding its share of perfume to scent the nostrils.
- I can barely wait for the Blueberry and Bilberry season to deliver the taste of my favourite fruit. I can’t think of a blue vegetable unless you count purple sprouting broccoli but if I have missed your favourite let me know.
- ‘Seeing red’ as a phrase could be replaced with ‘seeing blue’ when you consider some of the great blue flowering plants.